Risky Biz News: FBI disrupts AlphV/BlackCat ransomware;
In other news: Microsoft announces a more secure Windows print mode; FISA Section 702 gets a temporary extension; and MongoDB discloses data breach.
You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
The RiskyBiz crew behind our newsletters and podcasts is on hiatus between December 8 and January 8 for the winter holidays, but we put out this weekly edition with some of the past week's biggest infosec stories.
Happy holidays!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Cyberattack on Iranian gas stations: A hacktivist group known as Predatory Sparrow has crippled the payment systems of gas stations across Iran. The incident is believed to have impacted more than 2,000 of the country's gas pumps (~70% of all pumps). Iranian officials have confirmed the incident and claimed the group is a front for Israeli and US cyber operations. BBC Persia claims the incident had a sprawling impact across the country, even days after the attack.
Ledger incident: A threat actor has compromised the npm account of a former Ledger employee and added malicious code to a Ledger SDK meant to connect web apps to the Ledger backend. The malicious code emptied Ledger wallets on websites that used the compromised SDK. Losses are estimated to be around $600,000.
Comcast hack: US telco Comcast says that hackers exploited the CitrixBleed vulnerability to breach one of its systems and steal the personal information of almost 36 million customers. Comcast says the hack took place between October 16 and October 19, 2023
Mr. Cooper hack: Mortgage and lending company Mr. Cooper says the ransomware attack that hit its IT systems at the end of October led to the theft of personal data of almost 14.7 million customers.
Coin Cloud hack: Hackers claim to have stolen the personal data of more than 300,000 customers of now-defunct Bitcoin ATM provider Coin Cloud. The hackers claim the data also includes more than 70,000 pictures of customers taken using the ATMs' cameras. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
MongoDB hack: The company behind the MongoDB database has announced a security breach of its corporate systems. The breach took place on December 13, and attackers appear to have gotten their hands on some customer data. MongoDB says they have not seen any unauthorized access to customer cloud environments (so far).
Kyivstar attribution: A hacking group named Solntsepek took credit for the attack that crippled Kyivstar, Ukraine's largest mobile telco. Ukrainian officials have attributed the attack to a hacking unit linked to Russia's military intelligence service GRU. Solntsepek has been previously linked to Sandworm.
OKX crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen $2.7 million worth of crypto assets from OKX after they gained access to one of the platform's smart contracts keys.
Aurory crypto-heist: The Aurory cryptocurrency exchange has been hacked for $1.2 million worth of assets. The attacker apparently drained 80% of the company's liquidity pools. The platform has shut down all operations to investigate the hack.
NFT Trader crypto-heist: A threat actor exploited a vulnerability in the NFT Trader platform and stole $3 million worth of NFTs. NFT Trader blamed the bug on one of its third-party tools—like that would make their users feel better for some reason. The culprit seems to be the Flooring Protocol.
General tech and privacy
Windows Protected Print Mode: Microsoft has announced Windows Protected Print Mode (WPP), a more secure rewrite of the Windows print mode, the feature that allows the operating system to interact with printing devices. The new WPP mode was designed around the Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) and removes the need for third-party printing drivers, which are set to be phased out in the coming years. Microsoft says the new mode will be available for testing via Insiders builds and should work fine with most printers made in the last 10 years.
SAC in Windows 11: Germany's BSI has published a technical analysis of the new Smart App Control feature in Windows 11. It's in German, though.
Google Maps geolocation data update: Google has changed how its Maps app stores geolocation data. Going forward, Maps will store all user location data on the device instead of Google's servers. The company made the change after law enforcement agencies had been abusing geo-fencing warrants to mass-collect data on everyone who entered a specific geographical area, whether they were suspects or not.
Apple to require warrants for push notification data: Apple has updated its legal guideline [PDF] and will now require law enforcement agencies to obtain warrants for its users' push notification data. The new rules were put in place after a US senator exposed that law enforcement agencies from different countries were requesting push notification metadata from both Apple and Google as part of their investigations. [Additional coverage in The Verge]
Apple Stolen Device Protection: Apple is rolling out a new iOS feature named Stolen Device Protection that, when enabled, will require users to authenticate using Face ID or Touch ID before making changes to sensitive device settings. Besides requiring a facial scan or fingerprint scan, the Stolen Device Protection feature also adds a one-hour delay before changes are applied, allowing real device owners to still have access to their accounts and devices and prevent being locked out. [Additional coverage in MacRumors]
Passcode 5th Amendment: The Utah Supreme Court has ruled that suspects can refuse to hand over their phone passcode to police during an investigation. The court unanimously ruled that passcodes fall under the protection of the US Constitution's Fifth Amendment, which protects citizens from self-incrimination. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
NGO sues Adobe: A Dutch NGO has sued Adobe for using browser cookies to track the web activity of Dutch citizens.
Active Listening: Marketing materials from the Cox Media Group claim the company can tap into customer device microphones (smartphones, TVs, etc.) and listen to nearby conversations. Named Active Listening, the feature is touted as a way to improve ad delivery. [Additional coverage in 404 Media]
Firefox 121: Mozilla has released Firefox 121. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest changes in this release are Wayland-by-default on Linux and an option in the settings page to force Firefox to underline all links.
Weibo tells users to be careful: Chinese social media company Weibo has told users to avoid expressing pessimism about the economy.
Spam bots come to Mastodon: Several Mastodon instances have been dealing with a giant wave of spam accounts over the past week.
Dropbox AI drama: Dropbox has a new "AI" feature that will take your files and share them with OpenAI. Obviously, most users didn't know about it. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
Threads TOS drama: Mastodon server admins and their users are in shock to find out that Meta has given itself the right to scrape everyone's data and track their activity once Threads federates with Mastodon instances and anyone interacts with a single piece of Threads content. I kid you not!
Government, politics, and policy
EU starts Twitter investigation: EU officials have opened an official investigation into Twitter for "the dissemination and amplification of illegal content and disinformation in the EU, transparency of the platforms and design of the user interface." The investigation comes days after an Irish newspaper reported that Musk intentionally crippled the platform's ability to remove disinformation, CSAM, and other illegal content.
NCSC CEO leaving: The CEO of the UK NCSC cyber agency is leaving her post for a diplomatic post. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Pegasus in Poland: A Polish court has confirmed that Polish state TV service TVP used manipulated SMS messages that were stolen from an opposition leader using the Pegasus spyware. The report confirms—yet again—that the former Polish government used the Pegasus spyware in politically motivated operations rather than legitimate law enforcement operations. [Additional coverage in OKO Press]
China's incident classification tiers: The Chinese government is working on a four-tier system that will be used to classify cybersecurity breaches and related incidents. The four tiers are color-coded and go from blue to yellow to orange and then red based on an incident's severity and impact on citizens and national security.
China warns of foreign backdoors: The Chinese Ministry of State Security says an "extensive investigation" found backdoors in overseas geolocation software that was being used to collect data from Chinese firms. [Additional coverage in Reuters/non-paywall]
China's iPhone ban expands: More and more Chinese government agencies and state-controlled companies are imposing bans on using iPhones at work. The new ban has been described as a "major step up" from the initial ban in September, which only impacted the highest levels of the Chinese government. [Additional coverage in AppleInsider]
FISA S702 temporary renewal: US lawmakers have temporarily extended the FISA Section 702 surveillance powers until April 19, 2024, to give themselves more time to negotiate. Section 702 is expiring at the end of the year. [Additional coverage in The Record]
CISA SbD alert: CISA issued its third Secure by Design security advisory. This one urges software makers to stop using static default passwords for their products.
FCC adopts new data breach rules: The US Federal Communications Commission has adopted new data breach notification rules for US telcos. The new rules remove the need to notify users of a data breach if no harm is likely to occur, expand the scope of a breach to cover accidental data exposures to telco employees and their providers, add mandatory breach reporting to the FCC itself, and remove breach notification waiting periods—meaning telcos have to notify users as soon as possible.
Foreign election interference: The US ODNI has published a report detailing the foreign interference that took place during the 2022 US Midterm Elections. The report notes that while China interfered, it did so for both parties. On the other hand, Russia focused many efforts on trying to denigrate the Democratic Party and its support for Ukraine.
US Senate confirms Haugh: The US Senate has confirmed Air Force Lt. Gen. Timothy Haugh as the next head of the NSA and US Cyber Command.
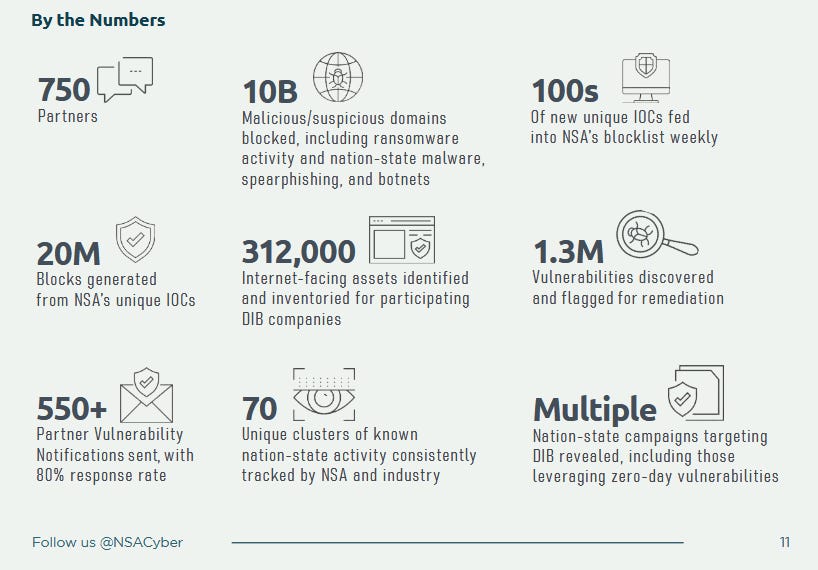
NSA cybersecurity year in review: The NSA has published its cybersecurity year-in-review report.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this podcast, Patrick Grey and Tom Uren talk about whether election interference will take place in the Taiwanese, US, and Russian elections that are all taking place in 2024. They also look at a ChatGPT-powered online harassment campaign.
Cybercrime and threat intel
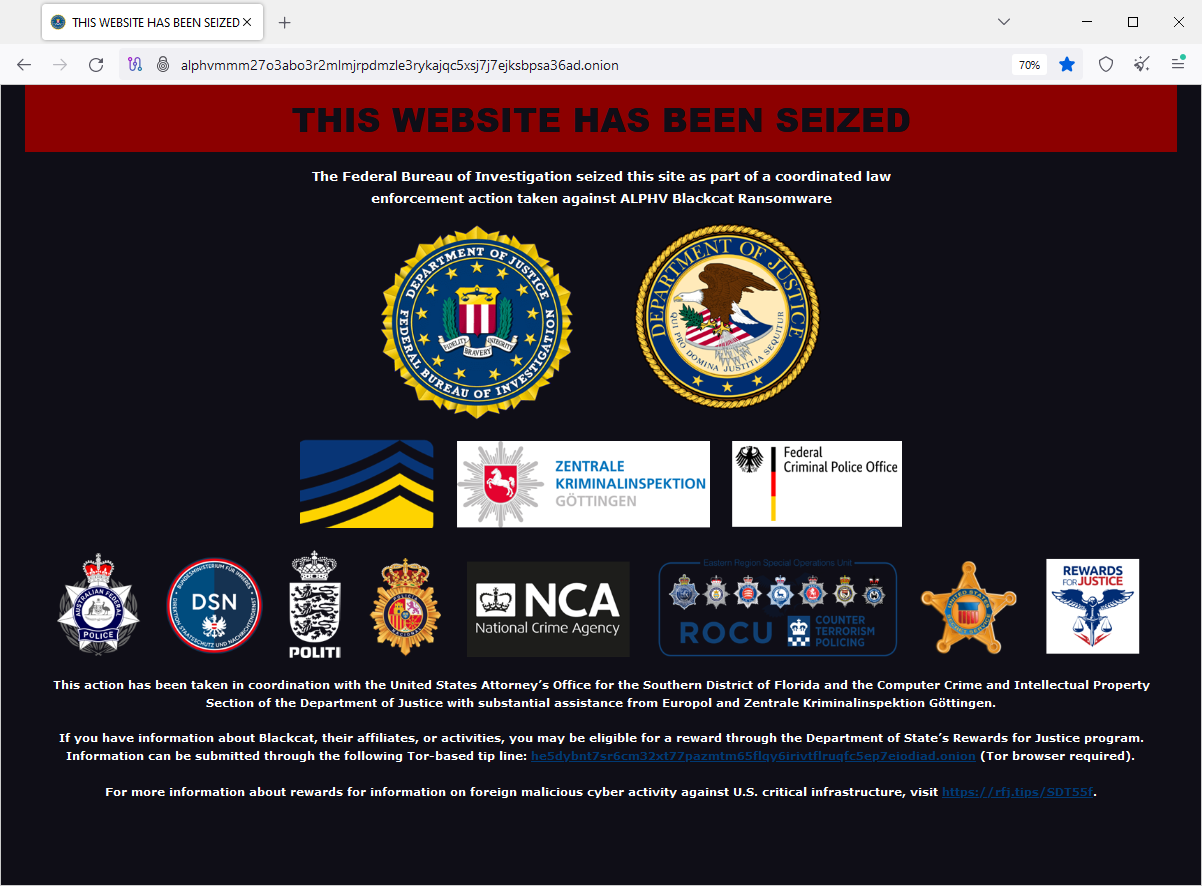
FBI disrupts AlphV ransomware: US authorities have hacked and seized server infrastructure operated by the AlphV (BlackCat) ransomware gang. Authorities say they also recovered 500 encryption keys, which they are now offering together with a decrypter to all affected victims. This confirms rumors from last week.
Pig-butchering gang detained: US authorities have unsealed charges against four suspects (detained two) for their role in a sprawling crypto-investment scheme (aka pig butchering) that netted them $80 million.
Nirvana Finance hacker pleads guilty: Shakeeb Ahmed, 34, of New York, pleaded guilty to hacking the smart contract of Nirvana Finance and stealing $12.3 million from the company and its users. US authorities said Ahmed was the first person arrested in the US for hacking a smart contract. Ahmed used to work for Amazon.
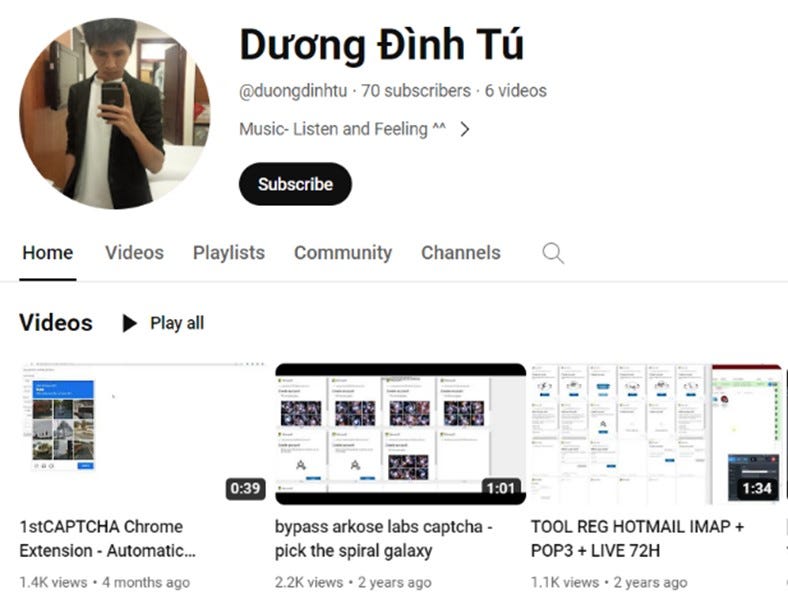
Storm-1152 disrupted: Microsoft took legal action to disrupt the server infrastructure of Storm-1152, a threat actor who created and sold access to more than 750 million Microsoft accounts. The accounts were used to help other bad actors avoid identity checks and carry out online fraud. In addition, the group ran a service to help crooks bypass online CAPTCHA tools. As part of the legal case, Microsoft named three Vietnamese men as Storm-1152 members. They were identified in court records as Duong Dinh Tu, Linh Van Nguyễn, and Tai Van Nguyen.
Qakbot returns: Several security researchers have spotted new activity from the Qakbot botnet, which US and European officials disrupted back in August. This comeback was first spotted by Censys at the end of November.
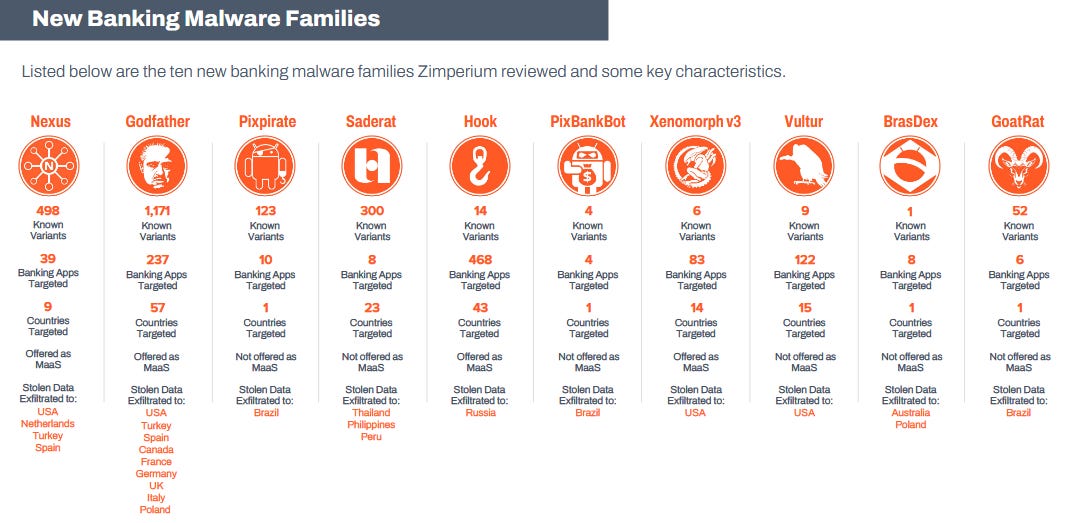
Mobile banking malware: Zimperium has published its yearly report on the mobile banking malware landscape. The company says it spotted 29 mobile banking malware strains this year, targeting more than 1,800 banking applications across 61 countries. The top banking malware was Hook, which targeted 618 e-banking apps. The most targeted country was the US, with 109 banks targeted.
Magento wish list exploit: Sansec researchers have documented a series of attacks against the wish list function of Magento 2 e-commerce sites.
Target hacker hunt: Infosec reporter Brian Krebs has managed to untie and unwind new knots in his hunt for the Target hacker, an individual known as Rescator.
Ransomware figures: According to court data, French authorities have started 512 ransomware-related investigations in 2023, representing a new report for the European country. On that note, both SentinelOne and Guidepoint have also published reports on recent developments from the ransomware ecosystem, covering numbers and recent tactics. [Additional coverage in ZDNet France]
Ransomware and the press: Sophos researchers look at how ransomware gangs have been using and interacting with journalists as part of their day-to-day operations and extortion campaigns.
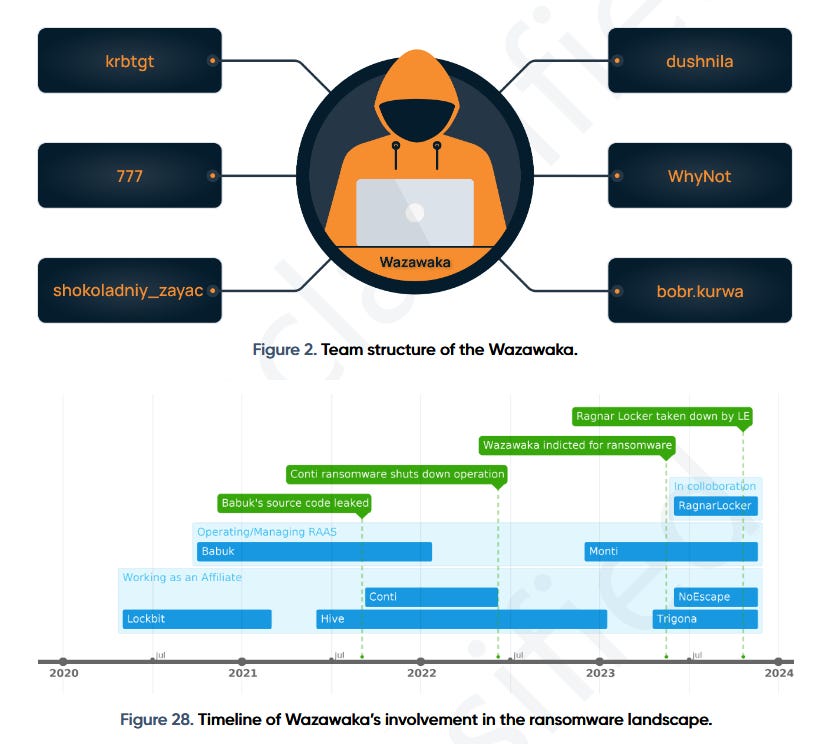
Wazawaka profile: Prodaft researchers have published a profile on Wazawaka, an infamous ransomware affiliate identified by US authorities as Russian national Mikhail Matveev. The report looks at Matveev but also his team, including other threat actors such as 777, bobr.kurwa, krbtgt, shokoladniy_zayac, WhyNot, and dushnila.
Malvertising campaign: Malwarebytes has been tracking malvertising campaigns leveraging Google search ads for stuff like WinSCP and Zoom to deliver payloads like PikaBot and the HiroshimaNukes or FakeBat loaders.
UNC2975: On the same topic, Google's Mandiant division looks at UNC2975, which the company describes as one of the largest clusters of malvertising activity today.
DarkSide member moves to malvertising: ConnectWise researchers have spotted a former member of the DarkSide ransomware gang delivering trojanized apps using malicious ads on search result pages.
Stockpiled domains: Palo Alto Networks says it identified more than 1.1 million stockpiled domains that are likely to be used in future malicious campaigns.
"Automation employed by attackers can leave traces of information about their campaigns in various data sources. Security defenders can find these traces in locations such as certificate transparency logs (e.g., certificate field reputation or timing information) and passive DNS (pDNS) data (e.g., infrastructure reuse or characteristics)."
OLVX: ZeroFox has published a report on OLVX, a new underground cybercrime shop selling access to hacked servers via shells, RDP, SSH, SMTP, webmail, cPanel, and others. The site also sells compromised accounts, combolists, and phishing kits.
8220 Gang: Imperva looks at the 8220 Gang—a cryptocurrency operation—targeting Oracle WebLogic servers with a new vulnerability tracked as CVE-2020-14883.
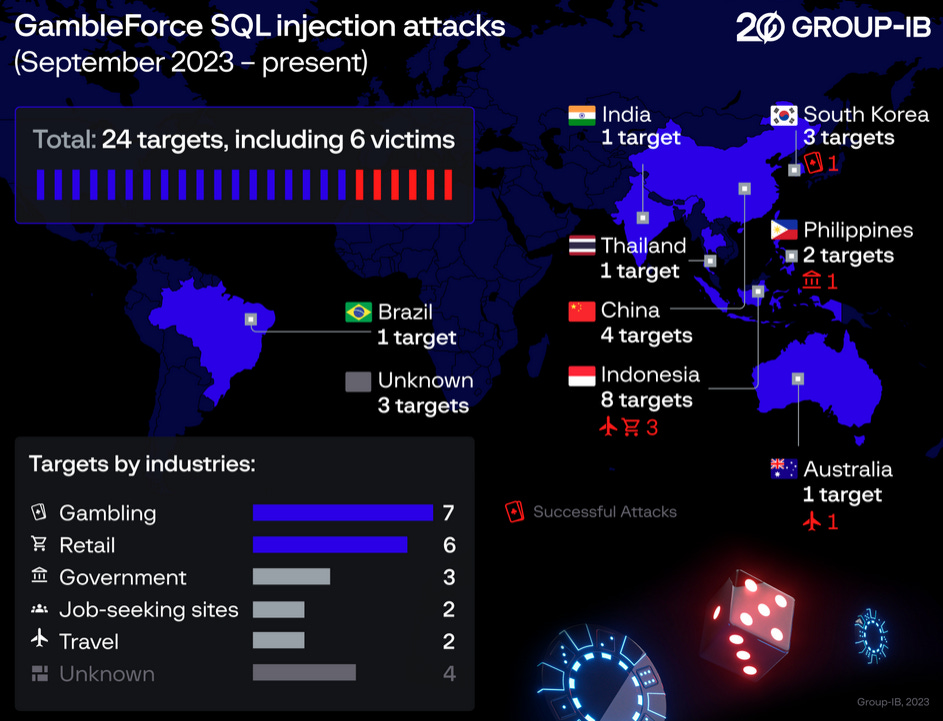
GambleForce: A new threat actor named GambleForce has been using SQL injection attacks to breach government and gambling sites in the APAC region.
Malware technical reports
NKAbuse: Kaspersky has identified a new botnet targeting Linux systems. Named NKAbuse, the botnet gets its name after its use of the NKN protocol for its C2 channel.
InfectedSlurs botnet: Akamai is seeing the InfectedSlurs botnet expand its attack arsenal and go after QNAP VioStor NVR devices using CVE-2023-47565.
Vetta Loader: Italian security firm YOROI has published a technical report on Vetta Loader, a new malware strain hitting Italy and spreading through infected USB devices.
BazarCall: Abnormal Security has seen a new wave of BazarCall phishing campaigns. The malware was in fashion in 2020-2021 but has somewhat lost steam in recent years.
Rhadamanthys: Check Point has published a technical deep-dive into the Rhadamanthys infostealer. Its latest version comes with additional spying features and a plugin system.
New banking trojan: IBM X-Force has looked at a new banking trojan—possibly related to DanaBot—employing a new web injection module that targets more than 40 banks across North America, South America, Europe, and Japan.
DanaBot: And since we're on DanaBot, OALABS has published some recent IOCs on the malware.
BatLoader and FakeBat: eSentire looks at two Russian Malware-as-a-Service platforms (BatLoader and FakeBat) and their recent operations abusing Google search ads.
BianLian: Security researcher Cryptax has published an analysis of the BianLian Android banking trojan (not to be confused with the ransomware operation).
Play and AlphV: CISA has published technical advisories on the Play and AlphV ransomware strains. According to CISA, AlphV asked for $500 million in ransoms and received nearly $300 million.
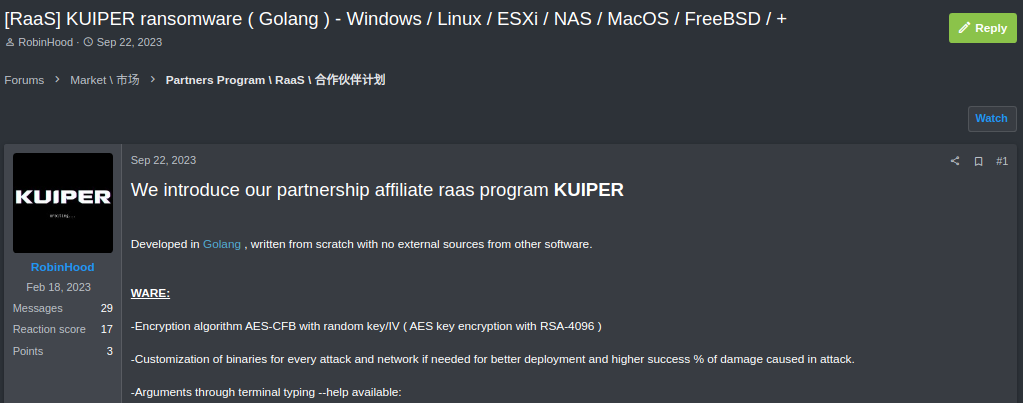
Kuiper ransomware: Stairwell looks at Kuiper, a new Ransomware-as-a-Service operation that has been advertised on underground forums since September.
Sponsor Section
In this product demo, GreyNoise founder and CEO Andrew Norris demonstrates how people use the GreyNoise sensor network.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
OilRig: ESET looks at four new OilRig downloaders, named SampleCheck5000, OilCheck, ODAgent, and OilBooster.
MuddyWater: Broadcom's Symantec looks at a MuddyWater (Seedworm) campaign targeting telcos in Egypt, Sudan, and Tanzania.
Gaza Cybergang: SentinelOne looks at Pierogi++, a new backdoor used by the Gaza Cybergang in 2022 and 2023 operations targeting Hamas opposition.
Sidewinder: CyFirma researchers look at SideWinder's macro malware arsenal. SideWidner, also known as Rattlesnake, is a suspected Pakistani APT group.
Kasablanka: Qihoo 360 looks at Kasablanka APT attacks targeting the Nagorno-Karabakh region with VenomRAT payloads.
DPRK recruitment ops: NISOS researchers look at online personas used by DPRK operators to fraudulently obtain remote employment from unwitting companies in the United States.
UAC-0177 (JokerDPR): Ukraine's CERT team has published IOCs for UAC-0177 (JokerDPR), the hacking group that claimed last year to have hacked Ukraine's Delta military communications platform. The group has also amplified Russian disinformation efforts about the war in Ukraine.
Calisto APT: Sekoia has published its own (previously private) report on how they identified Russian individual Andrey Korinets as a member of the Calisto (Star Blizzard, Cold River) APT—recently sanctioned by the UK and charged by the US.
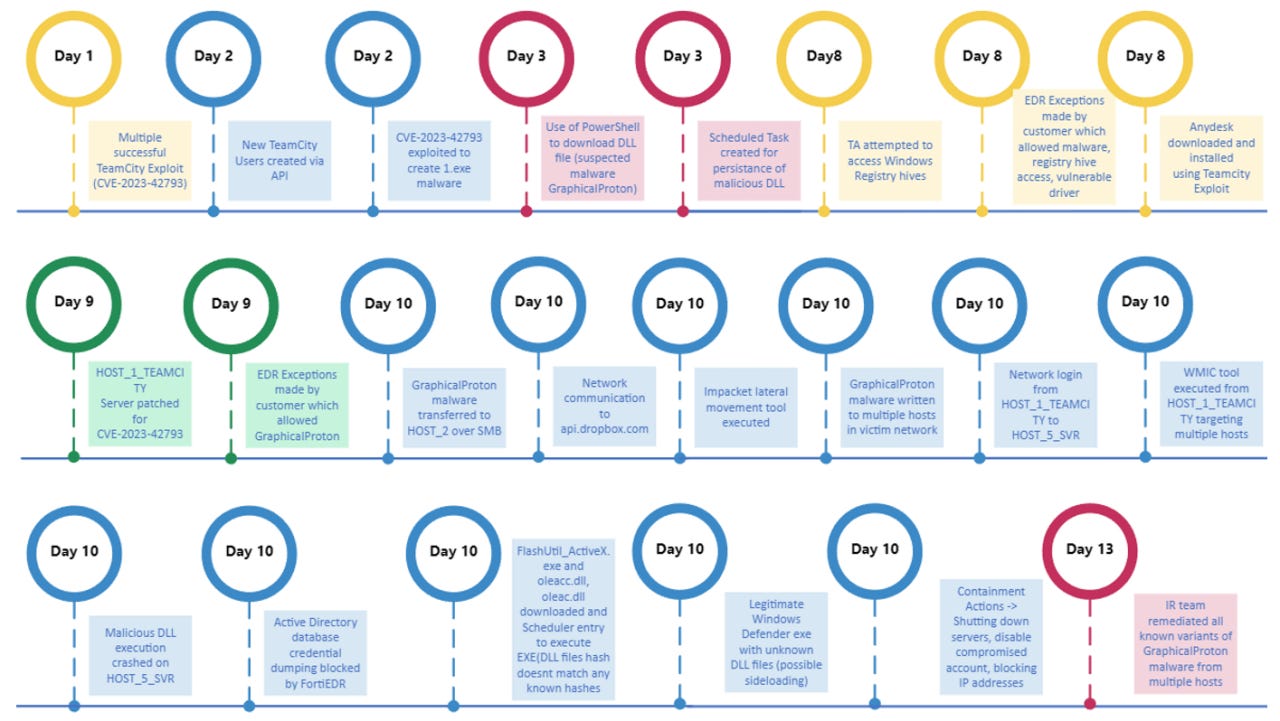
APT29 alert: CISA, the NCSC, and Poland's CERT team and SKW service warn that APT29 (linked to Russia's SVR intelligence agency) is exploiting a vulnerability (CVE-2023-42793) in JetBrains TeamCity servers for initial access to corporate and government systems. Fortinet and Logpoint also looked at the same attacks. According to the Shadowserver Foundation, more than 800 unpatched TeamCity servers were still connected online last week.
Volt Typhoon: Lumen has linked the new KV-botnet to the Volt Typhoon Chinese cyber-espionage group. Comprised of unpatched Cisco, Netgear, and Fortinet devices, the botnet has been used as a proxy and covert data transfer network.
"We assess from both our telemetry and open-source reporting, that the use of this botnet is limited to Chinese state-sponsored organizations. Thus far the victimology Black Lotus Labs has observed from the KV-cluster aligns primarily with a strategic interest in the Indo-Pacific region, having a particular focus on ISPs and government organizations. At least one user of the KV-cluster is Volt Typhoon, but Volt Typhoon is believed to operate over other obfuscation networks as well. We believe that it would be unlikely for the threat actor to repurpose this network to target lower valued networks and risk its discovery."
Chinese info-op targeting US: ASPI researchers have found a network of YouTube accounts pushing pro-Chinese and anti-US narratives and misinformation. Many of the videos used generative AI. The world of at-scale AI-generated misinformation is upon us.
Chinese info-op in Taiwan: In a different report, Graphika researchers say they found thousands of inauthentic accounts across Facebook, YouTube, and TikTok attacking pro-independence parties and pushing pro-Chinese propaganda in Taiwan ahead of the country's election in January 2024.
Another Chinese info-op: On the same front, ISD has seen new Spamouflage activity pushing pro-Chinese and anti-US narratives and misinformation.
Google info-op report: Google has published its quarterly report on influence operations on its websites. Lots of Chinese and Russian operations are mentioned.
TikTok info-ops: TikTok has published its Q3 threat report that looked at the influence operations the company spotted on its site. Six of the 16 campaigns were related to Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
ANSSI alert on telco attacks: France's cybersecurity agency has published a security advisory warning of increasing APT attacks targeting the telecommunications sector.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Zoom unveils VISS: Video conferencing software maker Zoom has unveiled VISS, a new vulnerability impact scoring system.
"By objectively measuring the impact of vulnerabilities from a defender's perspective, VISS can base its evaluations on responsibly demonstrated exploitation rather than theoretical threats."
Terrapin attack: A team of academics has published details on Terrapin, a new attack against the SSH protocol. The attack requires an AitM position but can be used to downgrade SSH connections to less secure states. SSH clients, such as SUSE and PuTTY, have been notified and are rolling out patches. The attack is tracked as CVE-2023-48795.
Marvin attack impacts Rust: The Marvin cryptographic attack was found to also impact Rust's RSA implementation.
Opera address bar spoofing: Opera's mobile browsers are vulnerable to a bunch of address bar spoofing attacks.
AWS WAF bypass: BCK Security researchers found and helped patch a bypass of the AWS WAF.
Unpatched GWT vulnerability: BishopFox researchers look at an eight-year-old and still unpatched vulnerability in the Google Web Toolkit framework.
Unpatched Google OAuth vulnerability: TruffleSecurity published details about a Google OAuth vulnerability that lets former employees retain access to corporate apps even after they've been off-boarded and removed from their employer's Google organization. Google has not patched the reported issue.
Perforce vulnerabilities: Microsoft has identified four vulnerabilities in Perforce Helix Core Server, a source code management platform widely used in the video game industry. The vulnerabilities include one unauthenticated RCE (CVE-2023-45849) with a 10.0 severity rating.
KingConnect vulnerabilities: White Oak Security has found four vulnerabilities in KingConnect routers, including an unauth RCE. KingConnect did not respond to the responsible disclosure process, so the bugs are unpatched.
Nagios vulnerabilities: NCC Group researchers have discovered 16 vulnerabilities in the Nagios XI remote monitoring toolkit.
Outlook RCE: Akamai has published a two-part writeup on two Outlook vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-35384 and CVE-2023-36710) that can be chained for RCE attacks on Outlook instances.
SMTP Smuggling: SEC Consult has published details on SMTP Smuggling, a new technique for spoofing emails while not breaking SPF checks. Email servers from Cisco, GMX, and Microsoft were found to be affected, all of which have released fixes or mitigations.
Mobile telephony vulnerability: Dvuln researchers have described a method through which attackers could abuse tel:// links in SMS messages to trick users into setting up unauthorised call forwarding on their devices.
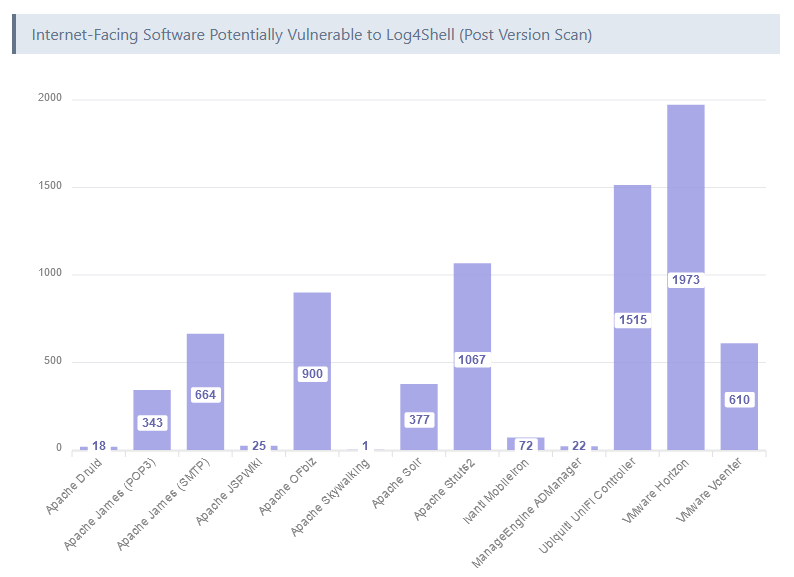
Log4Shell exposure shrinks: Research by VulnCheck has found that two years after its disclosure, very few systems are still exposed to attacks via the Log4Shell vulnerability.
"The current footprint of internet-facing software that is potentially vulnerable to code execution via Log4Shell is approximately 125,000 hosts. Of the 125,000 hosts, approximately 95% are using known patched versions. Although many predicted a long tail of exploitation, two years after disclosure, there are very few remaining Log4Shell initial access targets."
Infosec industry
Acquisition news: Identity provider Okta is acquiring Israeli cybersecurity startup Spera for at least $100 million.
MITRE EMB3D: The MITRE Corporation has launched EMB3D, a threat model specifically designed for embedded devices.
New tool—YARA-Forge: Florian Roth has launched a new project named YARA-Forge, a tool designed to streamline the process of sourcing, standardizing, and optimizing YARA rules.
New tool—SSH3: Belgian PhD student François Michel has open-sourced SSH3, a version of the SSH protocol that uses HTTP/3, QUIC, and TLS 1.3.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about recent hints that the Ukrainian government has figured out how to make use of the IT Army.