Risky Biz News: Russia blocks OpenVPN and WireGuard VPN protocols
In other news: Northern Ireland police deals with data breach; new TunnelCrack attack leaks VPN traffic; and a couple of crypto-wallet vulnerabilities.
This newsletter is brought to you by no-code automation platform Tines. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
Russian internet users are reporting that VPN clients using the OpenVPN and WireGuard protocols have stopped working as of this week.
The unofficial ban has been reported primarily by users of Russian mobile internet operators, such as Beeline, Megafon, MTS, Tele2, Tinkoff, and Yota.
OpenVPN and WireGuard traffic does not appear to be blocked on landline connections and especially on business accounts, where they're most likely to be used by the few foreign companies still doing business in Russia.
The Roskomnadzor, Russia's communications watchdog, has not formally confirmed the block, but the massive number of user complaints suggests the ban is more than a test and most likely applied nationwide.
Most reports say OpenVPN and WireGuard clients won't connect to foreign servers, but some scant reports also claim similar issues with ShadowSocks, another VPN protocol.
Two other protocols, IPSec and IKEv2, were blocked in May 2022, with similar blocks following for L2TP and PPTP.
According to Russian IT expert ValdikSS, the bans are enforced differently per Russian region, most likely related to local internet filtering and blocking capabilities.
VPN connections trying to connect to foreign servers are what's getting blocked. VPNing from abroad inside Russia still works, most likely not to disturb the operations of foreign business.
The Roskomnadzor has been actively trying to block VPN services inside Russia since the country's invasion of Ukraine. Access to VPN services has been seen as a major threat to the Russian government, which has tried to limit its citizens' access to accurate news about its military effectiveness in Ukraine, its war crimes, and the breakdown of its economy.
Initially, the Roskomnadzor tried outlawing VPN services, but when that didn't work, it began blocking the VPN protocols themselves.
Russian government officials have repeatedly stated they do not intend to criminalize the use of a VPN, but they have made it illegal to share advice on how citizens can skirt the VPN blocks. This way, Russian officials avoid the mess of criminalizing the IT departments of foreign companies but still get to go after unruly individuals and privacy advocates still opposing their draconic regime.
At one point, the government also launched an anti-VPN media campaign meant to scare away users from using the services.
On most Russian IT forums and Telegram channels, users are now flocking to tools used to evade China's Great Firewall and testing as alternatives.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
PSNI breach: The Police Service of Northern Ireland (PSNI) has suffered what it called a monumental data breach after it mistakenly published a list of all police officers on its website. The file exposed the names, ranks, roles, and locations of more than 10,000 offers and civilian staff. Officials blamed the leak on a human error after a spreadsheet containing the sensitive data was uploaded on its Freedom of Information (FoI) websites. Even if the file was available online for only three hours, the PSNI is now looking to relocate some of its staff, especially officers that had been working with the MI5 intelligence service on sensitive investigations.
Hundred Finance shuts down after hack: The Hundred Finance cryptocurrency platform is shutting down after it got hacked and lost $7.4 million worth of customer assets in April this year. The shutdown is part of a community-voted plan to compensate victims of the hack. The company says the hack impacted its "ability to effectively perpetuate [its lending] protocol."
Steadefi crypto-heist: The Steadefi crypto platform has lost almost $1.1 million after a hacker obtained a private key for one of its wallets. The company says it recovered around $418,000 worth of stolen assets, but the rest remain under the hacker's control.
Dallas ransomware attack: The Dallas City Council approved $8.6 million in payments for services related to a ransomware attack the city's IT network suffered earlier this year, in May. At the time, the city refused to pay the attackers and chose to restore its IT systems. The payments approved this week cover costs with new hardware, software licenses, consulting, forensics, and credit monitoring for individuals who had their personal data stolen. The city is planning to file insurance claims to cover the costs. The Royal ransomware operation took credit for the intrusion.
General tech and privacy
RCS goes E2EE: Google has announced that all RCS conversations in its "Messages by Google" app are now end-to-end encrypted.
Project IDX: Google has released Project IDX, a cloud-based IDE with today's favorite hype technology, AI.
Yandex leak: Ad security platform Confiant has published an analysis on the Yandex source code that was leaked online earlier this year. The report covers how Yandex collects and tracks users online. The tl;dr is that the company has loads of data on foreigners, and its anonymization system isn't that good, allowing for pretty accurate re-identification and tracking. The Russian state is also elbows-deep in the company.
"The matcher process is clear evidence that at least some of the data collected by Yandex could be synced with Russian state owned entities. Yandex also appears to be very, very close to becoming state controlled or nationalized, and it is about to be required to share international user data from its taxi services with the FSB. "
Microsoft 365 in Russia: Microsoft is notifying Russian customers that it will no longer be possible for Russian companies to pay for Microsoft 365 subscriptions after September 30 this year. Microsoft says it already suspended license renewals on July 1 and will honor existing licenses until their expiration date. The move comes after Microsoft had already pulled many services from Russian companies and, at one point, had blocked Russian users from downloading new versions of its OS from its official website. [Additional coverage in DP]
Government, politics, and policy
US AI cyber contest: The White House and DARPA have announced a two-year contest designed to improve the security of AI systems. Named the AI Cyber Challenge (AIxCC), the contest will provide security researchers with access to cutting-edge technology from the world's leading AI companies, such as Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI. The contest will include a prize pool of up to $20 million, with a $4 million top prize. The DEFCON security conference will host the contest's semi-finals next year and the final at its 2025 edition. Twenty spots are available for the semi-finals and five for the finals.
RFI on FOSS and memory-safe languages: The White House Office of the National Cyber Director (ONCD) has asked the public and private sectors to provide feedback on possible regulation on the use of open-source and memory-safe programming languages.
Canada exposes WeChat disinfo campaign: The Canadian government says a coordinated WeChat disinformation campaign targeted Michael Chong, a Member of the Canadian Parliament and a staunch critic of the Chinese Communist Party. Officials say the campaign spread falsehoods about Chong, his family, and his political stances around May of this year. Canadian officials say they don't have evidence, but they believe the Chinese government involvement was "highly probable."
Indian military to replace Windows: The Indian Ministry of Defense will replace its fleet of Windows computers with Maya OS, a local Linux variant. The new operating system is currently being developed by multiple Indian government agencies. Work on Maya began in 2021, and the new operating system is a modified version of Ubuntu, today's most popular Linux desktop OS. India now joins China, Russia, and North Korea as countries that are developing their own Linux variants to replace Windows on government systems. [Additional coverage in The Hindu/ h/t Ravy Nayyar]
India passes data privacy bill: The Indian Parliament has passed the country's first data privacy bill that sets rules for how tech companies can collect and store the data of Indian citizens. Companies will be allowed to store data abroad on the condition they honor law enforcement investigations, requests for content blocking from the government, and user data erasion requests. In case of non-compliance, the bill includes fines of up to $30 million for violations. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Tines co-founder and CEO Eoin Hinchy about how organizations can maximize the potential of their security teams during an economic downturn, with a concentration on why human error and burnout caused by excessive workloads on security teams can be a risk.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Lolek bulletproof hoster seized: US and Polish authorities have seized the domain of the Lolek bulletproof hosting provider. Prior to its takedown, the service has been operating since 2009. The service has been operating with a no-log policy, taking cryptocurrency payments, and has hosted cybercrime and extremist content. One of its downstream-hosted sites included the infamous KiwiFarms forum. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Russian hacker sentenced: A Russian court has convicted a hacker from Krasnodar for developing malware, stealing card data from foreigners, and... drum-roll... donating money to Alexei Navalny's Anti-Corruption Fund. Too bad Russia doesn't prosecute all the other hackers that didn't donate to Navalny.
Scattered Spider: Avertium researchers have published a report on Scattered Spider, a financially-motivated group also known as UNC3944 or 0ktapuss.
Lapsus$: The US DHS Cyber Safety Review Board (CSRB) has published its long-awaited report on the Lapsus$ gang. The CSRB started working on the report last December. The report looked at the gang's (simple) techniques and made 10 recommendations on how companies can defend themselves.
EvilProxy campaign: Proofpoint says a threat actor has been using a phishing toolkit named EvilProxy to intercept login credentials and MFA challenges, hijack accounts, and commit financial fraud. The campaign has been going on since March and has targeted high-level executives at hundreds of companies across the globe. Proofpoint says the campaign was fully automated, with attackers hijacking accounts seconds after a successful phish. The security firm believes the threat actor might be based in Turkey after they've seen it trying to avoid infecting victims from the country, even by accident.
K8s crypto-mining campaign: Cloud security firm AquaSec says it identified more than 350 organizations and open-source projects running misconfigured Kubernetes clusters. Researchers say the clusters were left exposed on the internet and that roughly 60% were compromised with a cryptominer. At least five crypto-mining campaigns were observed compromising systems.
Xurum campaign: Akamai is tracking a website hacking campaign named Xurum that uses a 2022 vulnerability to breach Magento 2 online stores. The attacker hijacks the store and then uses the Dirty COW exploit to take over the underlying Linux server. From there, the attack plants a JavaScript skimmer on the site to collect payment card details from customers paying for goods.
Capra campaign: Security firm Human has a breakdown of a new account takeover attack pattern they've detected in the wild against online betting platforms. The company named this campaign Capra, after the name of the threat actor's store, where the hacked accounts were being sold.
Moq data collection issue: An extremely popular NuGet package named Moq has been caught harvesting email addresses from a developer's local Git config file and sending the hashed data to a cloud server. The malicious behavior has been linked to SponsorLink, a toolkit that unlocks features inside open-source projects for donors and sponsors. Moq developers have removed the SponsorLink package from the library's latest version, but by this point, the email addresses of most of their users have already been harvested.
Malware technical reports
WHIRLPOOL: CISA has released a malware report on WHIRLPOOL, a new backdoor variant found deployed on hacked Barracuda email servers. It previously released another report on three other backdoors.
New Freeze.rs Rust injector: Fortinet looks at a new Rust-based injector named Freeze[.]rs used in malware campaigns this year.
DroxiDat: Kaspersky published a report on DroxiDat, a new version of the SystemBC backdoor that was deployed in a South African nation's critical infrastructure. The Russian security firm says the intrusion looked like the precursor of a ransomware attack, but ransomware was never deployed on the victim's network.
Statc Stealer: Zscaler has discovered a new infostealer named Statc Stealer. It is already used in the wild via malvertising and SEO poisoning campaigns.
Electron-based stealer: Mend researchers have discovered a new Electron-based stealer hidden inside malicious npm libraries.
Rhysida ransomware, Vice Society connection: Check Point has published a report on the new Rhysida RaaS, which the company believes may be tied to the operators of the older Vice Society ransomware. A separate report on the same Rhysida group was also published by Cisco Talos.
GootLoader: Trustwave says it saw a noticeable surge in GootLoader malware detections.
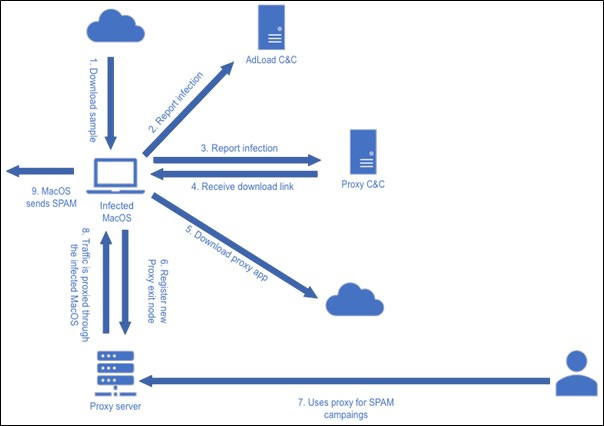
AdLoad gets a proxy module: AT&T's security team has spotted a new version of the AdLoad macOS adware strain that is now installing a proxy component on infected hosts. Systems infected with this component are turned into proxy exit nodes in a residential proxy botnet, allowing threat actors to funnel malicious traffic through the systems of unsuspecting users. Some of the analyzed traffic suggests the infected systems are being used to send out email spam campaigns. AT&T estimates the number of users infected with this new AdLoad variant to be in the thousands.
Sponsor Demo
In this demo, Tines CEO and co-founder Eoin Hinchy demos the Tines no-code automation platform to RiskyBiz host Patrick Gray.
APTs and cyber-espionage
Charming Kitten: The German Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV) says it detected "concrete spying attempts" by Iranian APT group Charming Kitten targeting dissident organizations and Iranian nationals living in Germany. Targets included lawyers, journalists, and human rights activists. The campaign has allegedly been taking place since the end of 2022.
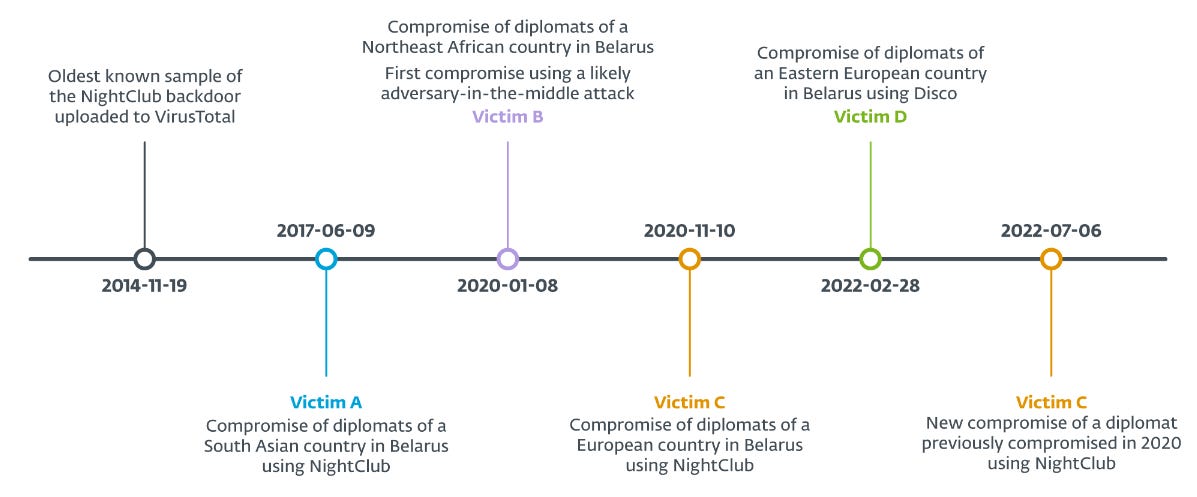
MoustachedBouncer: Security firm ESET has discovered a new APT group that has been conducting cyber-espionage operations against foreign embassies inside Belarus. Named MoustachedBouncer, the group has operated under the radar for at least nine years since 2014. The group's primary toolkit is a malware framework named NightClub and a backdoor named Disco. Some of the group's 2020 operations also involved the use of Adversary-in-the-Middle techniques at the ISP level, which has led ESET to believe that the group may be closely associated with the Belarusian government. Further evidence suggests the group may be cooperating with another APT named Winter Vivern.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
VS Code token stealing: Cycode researchers have found a way to decrypt, recover, and steal tokens stored inside VS Code's isolated storage space. The mechanism can allow malicious VS Code extensions to steal the tokens of other extensions and access their resources.
Synology, Western Digital NAS vulnerabilities: Claroty researchers have identified vulnerabilities in NAS products from Synology and Western Digital that expose the devices to credential thefts, remote code execution, and user data theft. All issues have been patched, and WD went as far as to ban devices from accessing its cloud service if they're not running the latest firmware.
Sogou vulnerabilities: CitizenLab researchers have found vulnerabilities in the custom-made encryption scheme used by Sogou Input Method, a popular Chinese keyboard app. Researchers say the vulnerabilities allow a threat actor to decipher user keystrokes in real-time as they're sent to the app's servers. The app is installed on more than 450 million devices. A fix has been released for its Android, iOS, and Windows versions.
"These findings underscore the importance for software developers in China to use well-supported encryption implementations such as TLS instead of attempting to custom design their own."
Milk Sad vulnerability: A threat actor has exploited a vulnerability in a popular Bitcoin library named Libbitcoin Explorer to recover seed phrases and steal funds from cryptocurrency wallets. Named Milk Sad (CVE-2023-39910), the vulnerability has been exploited since at least May, with attacks peaking around July 12. Researchers say Milk Sad is similar to two other crypto wallet vulnerabilities that were exploited in the wild in November 2022 and April 2023. It is unclear if the same attacker has been behind all three. A lookup utility has been set up so crypto-wallet owners can check if the SHA-256 hashes of their seed phrases are vulnerable.
BitForge vulnerabilities: At the BlackHat security conference, security researchers from Fireblocks have disclosed two vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-33241 and CVE-2023-33242) in cryptographic protocols used by MPC crypto-wallets that can allow a threat actor to recover seed phrases and steal an owner's funds. The two vulnerabilities are collectively known as BitForge and affect cryptographic protocols such as GG-18, GG-20, and Lindell 17. Crypto wallets from Binance, Coinbase, and Zengo have been confirmed to be vulnerable and have rolled out patches. Dozens of other wallet providers also use the protocols and are believed to be impacted as well. A lookup utility has been made available.
TunnelCrack attack: A team of academics has discovered vulnerabilities in almost all modern VPN products that can leak traffic outside of the protected VPN tunnel. Collectively known as TunnelCrack, the vulnerabilities can be exploited when a VPN user connects to a malicious WiFi network. TunnelCrack does not break the VPN encryption but works by tricking the VPN into sending traffic to attacker-controller IP addresses. VPN products from Mozilla, Microsoft, Cloudflare, Surfshark, and Windscribe are known to be vulnerable, and most have released patches.
Infosec industry
Windows Server 2012: 0Patch has announced plans to provide third-party security updates for Windows Server 2012 (and R2) once they go EoL later this year in October.
Acquisition news: Check Point has agreed to acquire Security Service Edge (SSE) company Perimeter 81 for $490 million on a cash-free, debt-free basis.
Rapid7 layoffs: Pen-testing giant Rapid7 is restructuring its operations and laying off roughly 18% of its workforce, the company disclosed in an SEC filing. More than 500 employees are expected to lose their jobs, and the company plans to permanently close some office locations. News of the layoffs was included in the company's Q2 2023 results, which reported a strong $751 million in recurring revenue, a 14% YoY growth.
NCC layoffs: UK security firm NCC is laying off additional staff, just six months after it cut 7% of employees across Europe and North America.
New tool—Mellon: Security firm BishopFox has open-sourced a tool named Mellon for executing attacks on devices supporting the Open Supervised Device Protocol (OSDP), such as RFID badges, smart cards, security cards, and other access control devices. The tool
New tool—Nemesis: Security firm SpecterOps has open-sourced a tool named Nemesis, a centralized data processing platform that ingests data produced during offensive security assessments.
New tool—Konstellation: Security firm Praetorian has open-sourced a tool named Konstellation that can enumerate cloud resources and find overprovisioning and privilege escalation paths.
New tool—DeRF: Security firm Vectra has open-sourced a tool named DeRF, an adversary and attack emulation framework.
New tool—EmploLeaks: Earlier this year, security firm Faraday open-sourced a tool named EmploLeaks, an OSINT tool that helps detect members of a company with leaked credentials.
New tool—YAMA: JPCERT/CC has open-sourced a tool named YAMA, which stands for Yet Another Memory Analyzer.
Pwnie Awards 2023: The Pwnie Awards were handed out this week at the Black Hat security conference in Las Vegas. There's no official announcement, but we did manage to put together a list of known winners based on toots and tweets we've seen so far.
Lamest Vendor Response: Threema, for its response to an ETH Zurich research paper that looked at vulnerabilities in its cryptographic protocols.
Epic Fail: The US TSA for leaving its No-Fly List exposed online.
Epic Achievement: Google TAG's Clément Lecigne for discovering 33 zero-days exploited in the wild since 2014, with eight in 2023 alone.
Most Underhyped Research: ZDI researcher Simon Zuckerbraun for his research on context cache poisoning.
Most Innovative Research: Thomas Roth, also known as GhidraNinja, for developing an iPhone JTAG cable called the Tamarin Cable and a Lightning Fuzzer for fuzzing iOS.
Best RCE: Simon Scannell, for an RCE in Cisco's ClamAV (CVE-2023-20032).
Best Cryptographic Attack: Ben Nassi and his team for an attack that recovers secret keys from power LED flickers.
Best Desktop Bug: B2ahex for CVE-2022-22036, a Windows EoP that abuses performance counters.
Lifetime Achievement Award: Peter "Mudge" Zatko.
Most Under-Hyped Research: ???
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq ask whether Chinese operations are becoming stealthier and why. Is it a top-down directive to be careful, or do the operations themselves require more stealth?