Risky Biz News: CISA establishes ransomware warning pilot program
In other news: Russian government to build its own GitHub alternative; Euler Finance hacked for $197 million; the UK government creates new security agency to defend against state-sponsored threats.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has officially launched this week the Ransomware Vulnerability Warning Pilot (RVWP) program.
CISA says this new program will have two main tasks. The first is to proactively scan the networks of critical infrastructure entities in order to identify systems that are vulnerable to common entry vectors used by ransomware gangs.
The second is for CISA to notify companies of their exposure and help secure vulnerable systems before they get hacked. CISA says the notifications will be made by regional staff members, either by email or phone call.
Although they announced it this week, the agency says the new RVWP program already started operations on January 30 this year.
CISA launched the RVWP program under the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022 (CIRCIA), which President Biden signed into law in March 2022.
On a personal note/advice, while RVWP is an admirable attempt to boost security across US critical sector companies, please don't cancel your vulnerability management licenses. It's not a panacea.
Breaches and hacks
Euler Finance crypto-heist: DeFi platform Euler Finance was hacked for $197 million worth of cryptocurrency assets after a threat actor exploited a vulnerability in its codebase. In a post-mortem of the hack, Euler says the threat actor used a flash-loan attack and a bug in its donations feature to exfiltrate legitimate funds they loaned from the platform to an account they controlled. According to a blockchain investigator named ZachXBT, the Euler exploiter is most likely a malicious entity and not a security researcher, as they also tried to exploit other platforms in the past months. The Euler hack ranks as the 26th largest cryptocurrency heist of all time.
STALKER 2 extortion update: In our last edition, we covered how a Russian hacker was trying to extort Ukrainian gaming company GSC Game World, threatening to leak content from its upcoming game unless the company apologized to Russians and re-added its Russian language pack back to the game. Let's just say that GSC is not having it, and they don't care about the hacker's threats since they have more important things to deal with, such as missile strikes from their "friendly neighbor.":
"We are a Ukrainian company, and like most Ukrainians, we have experienced many things that are much more terrifying: destroyed houses, ruined lives, and the deaths of our loved ones. Attempts to blackmail or intimidate us are completely futile."
Amazon Ring security incident: The ALPHV (BlackCat) ransomware gang claims to have breached Ring, an Amazon-owned company that makes highly popular smart doorbells and security cameras. Amazon told Motherboard they have no evidence a ransomware attack took place, but the company did not rule out data theft and a possible subsequent extortion attempt.
Marshall Amps ransomware incident: The Black Basta ransomware gang has taken credit for breaching the network of Marshall, a British musical instruments company mostly known for its electric guitar amps.
Saint Kitts and Nevis ransomware incident: The RansomHouse ransomware cartel has taken credit for an attack on the government of the Caribbean nation Saint Kitts and Nevis. This is the same ransomware gang that hit the Pacific state of Vanuatu in November of last year, an incident the country needed months to recover. Saint Kitts and Nevis officials have yet to confirm the incident.
General tech and privacy
Kali Linux Purple edition: The Kali Linux project has released Kali Purple, a version of the Kali Linux operating system that includes features and toolkits typically used by defensive security teams, also known as blue or purple teams. More than 100 defensive tools are included with the new Kali Purple distro, such as Elasticsearch SIEM, CyberChef, Suricata IDS, and more.
Government, politics, and policy
New UK National Protective Security Authority: The UK government has announced this week the creation of a new security agency. Named the National Protective Security Authority (NPSA), the agency will be tasked with helping UK businesses combat national security threats, such as state-sponsored attempts to steal their research and sensitive information. According to the UK government, the new NPSA will absorb the responsibilities of the Centre for the Protection of National Infrastructure, will operate under the MI5, and collaborate with the National Cyber Security Centre and the National Counter Terrorism Security Office.
Russian to build GitHub alternative: The Russian Ministry of Digital Development wants to use a reserve it created 16 years ago to fund a Russian source code hosting platform. To build its GitHub-like clone, the Russian government has chosen ANO Open Source, a non-profit organization that counts VKontakte, Rostelecom, and the Innopolis University as its founders. The total investment is 1.3 billion rubles ($17.2 million). The Chinese government took a similar approach, and most Chinese developers today are storing their code on a platform named Gitee. [More in Vedomosti]
Estonia parliamentary elections targeted by cyberattack: Estonia's parliamentary elections were unsuccessfully targeted by cyberattacks, one of the country's leading cybersecurity officials told The Record. The elections, which took place earlier this month, marked the first time that the majority of Estonian citizens cast ballots using the country's internet voting system. The official declined to offer a detailed description of the attacks or the threat actors but said that nothing out of the ordinary happened.
"There's no point in calling for a press conference and going and saying that this happened. Nothing out of the ordinary happened, nothing happened that hasn't happened the week before, or the week before that."
DOD cyber budget: The US Department of Defense is committing $13.5 billion to cyberspace activities, according to the Pentagon's budget for the fiscal year 2024. This year's DOD budget is also the first time CYBERCOM has used its newly acquired enhanced budgetary control powers to control its budget, DefenseScoop reports. The budget also includes funding for five additional Cyber Mission Force teams, which conduct offensive, defensive, intelligence, and support operations on behalf of CYBERCOM. The agency started with 133 Cyber Mission Force teams in 2012, and with the new addition, that number will go up to 147.
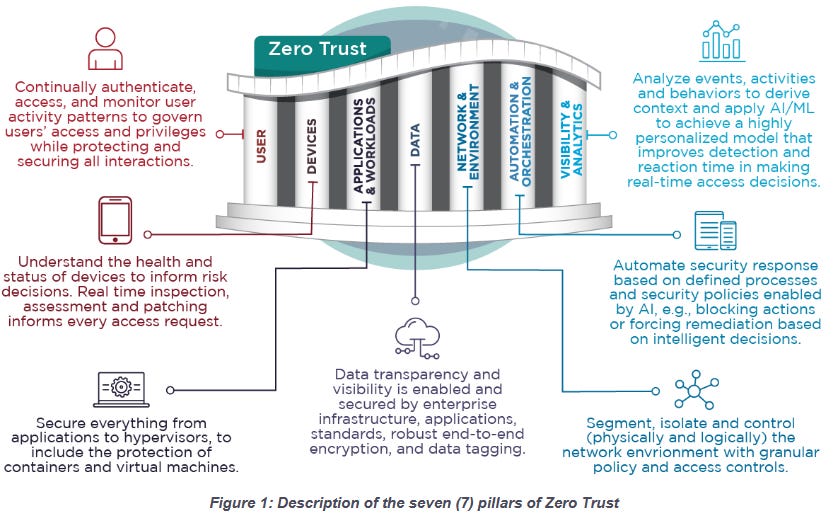
NSA guide on Zero Trust: The US National Security Agency has published a guide to help organizations integrate the Zero Trust framework into their identity, credential, and access management (ICAM) capabilities.
Risky Business Demo
In this Risky Business demo, Tines CEO and co-founder Eoin Hinchy demonstrates the Tines no-code automation platform to host Patrick Gray.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Sberbank issues fraud warning: Sberbank, one of Russia's largest banks, is warning that fraudsters are calling unsuspecting customers as part of a complex scheme where they pose as FSB or police officers. The fraudsters claim a bank employee transferred money from their accounts as a donation to the Ukrainian Armed forces, which could get account owners charged with high treason. The fraudsters' scam is to convince the customers to transfer the rest of their funds to a new account where police officers can monitor and catch the rogue Sberbank employee. In reality, customers are transferring money to the scammers and losing all their funds.
SVB phishing activity: Phishing campaigns that are trying to exploit the SVB collapse are well underway. Several threat actors have been spotted contacting companies, claiming to be business partners, and trying to redirect future payments to accounts they control, using the simple yet very convincing ruse that "SVB collapsed, please send money to our new bank account here."
Spike in crypto investment scams: The US Federal Bureau of Investigation issued a public service announcement this week warning about a spike in cryptocurrency investment schemes. The FBI's PSA comes after the agency published its yearly Internet Crime Report last week, the first edition of the report where BEC schemes were dethroned for the number one spot by—you guessed it—investment schemes.
Emotet's return: Trend Micro has its own report on Emotet's recent return. Similar reports are available from DeepInstinct and Cofense.
DEV-1101: Microsoft says that a threat actor it tracks as DEV-1101 is responsible for developing and selling access to several real-time reverse-proxy phishing kits. Also known as attacker-in-the-middle (AiTM) phishing kits, these toolkits can help threat actors intercept session cookies and bypass multifactor authentication (MFA). Microsoft says that since May 2022, DEV-1101 has been renting access to multiple AiTM phishing kits through ads on Telegram and underground hacking forums. Access to the phishing kits is now offered for $300/month, and a new feature allows threat actors to manage phishing campaigns via a Telegram bot rather than a dedicated web panel. Microsoft says DEV-1101's tools are widely used by multiple threat actors, accounting for "millions of phishing emails per day."
Malware technical reports
BatLoader: eSentire has a report on a BatLoader campaign abusing Google Search ads to infect victims and later drop Ursnif and the Vidar Stealer.
FakeCalls: Check Point has discovered a new Android trojan named FakeCalls, currently active in South Korea. CheckPoint says the malware is hidden inside Android apps that mimic more than 20 local financial institutions. Threat actors use the app to show too-good-to-be-true loan offers to victims and then close the deal by placing calling the victim and posing as bank employees.
QvoidStealer: OALABS published a series of IOCs for QvoidStealer, a .NET infostealer available on GitHub.
Sponsor Section
Airlock Digital is one of this newsletter's four main supporters and this week's featured sponsor. Earlier this year, in May, Airlock Digital CEO David Cottingham held a product demo with Patrick Gray, the host of the main Risky Business podcast, showing how Airlock's allow-listing product works.
APTs and cyber-espionage
2022 APT report: Chinese security firm QiAnXin has published its yearly APT threat report for the year 2022. The report is different from what you see from western firms since it focuses on threats targeting China. For example, one of the report's main revelations is that QiAnXin spotted foreign APts using six zero-days in Chinese software products to target Chinese organizations. QiAnXin says it recorded 331 APT-linked incidents last year and is currently tracking over 137 named threat groups. Two North Korea APTs, the Lazarus and Kimsuky groups, were the most active threat actors last year. The Beijing capital region accounted for most attacks, while government departments and the defense and military industry were the most targeted sectors.
Kimsuky APT: AhnLab has a report on a suspected Kimsuky operation distributing malware via an interview questionnaire related to North Korean topics.
Tick APT: ESET has discovered that a Chinese APT group commonly known as Tick breached in 2021 the network of an East Asian company that makes data-loss prevention (DLP) software. ESET says Tick compromised the company's internal update server and used it to deliver malware inside its internal network. In addition, ESET says Tick operators also deployed trojanized installers of legitimate inside the company's network. When the company's employees used these tools to provide tech support services, Tick also gained access to the company's customer networks as well. ESET says at least two of the company's customers were compromised this way. The ESET report documents the three new malware strains the group used in their operation.
Armageddon APT: ThreatMon published a report summarizing the Armageddon APT's attacks against Ukraine.
YoroTrooper APT: Cisco Talos has identified a new Russian-speaking threat actor. Named YoroTrooper, the group has been active since at least June 2022 and appears to be exclusively focused on cyber-espionage operations. The targets of YoroTrooper campaigns are government and energy organizations in Azerbaijan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and other CIS countries. The group primarily focuses on stealing app credentials, browser histories & cookies, and system information from compromised hosts.
"Our assessment is that the operators of this threat actor are Russian language speakers, but not necessarily living in Russia or Russian nationals since their victimology consists mostly of countries in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). There are also snippets of Cyrillic in some of their implants, indicating that the actor is familiar with the language. Also, in some cases, the attackers are targeting Russian language endpoints (with Code Page 866), indicating a targeting of individuals speaking that specific language. Espionage is the main motivation for this threat actor, according to the tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) we have analyzed."
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was also the March 2023 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates being released by Adobe, Microsoft, Mozilla Firefox, Citrix, and SAP. The Android project, Chrome, and Fortinet released security updates last week as well. This month, Microsoft patched 104 vulnerabilities, including two zero-days (CVE-2023-23397 and CVE-2023-24880). Microsoft credited Ukraine's CERT team for discovering the first zero-day, an elevation of privilege in the Outlook client that was exploited by "a Russia-based threat actor [...] in targeted attacks against a limited number of organizations in government, transportation, energy, and military sectors in Europe." Microsoft credited Google TAG for discovering the second zero-day, a Mark of the Web (MOTW) bypass that was exploited by the Magniber ransomware gang. On the same note, Adobe also patched its own zero-day, tracked as CVE-2023-26360, and targeting Adobe ColdFusion.
Akuvox vulnerabilities: Claroty researchers have identified 13 vulnerabilities in the firmware of the Akuvox E11 smart intercom and doorbell system. The vulnerabilities can allow hackers to execute code remotely on the device in order to activate and control its camera and microphone, steal videos and images, or gain a network foothold for other attacks. Akuvox says it will have firmware updates by March 20.
Dolibarr RCE: DSEC Bypass researchers have found an unauth SQLi vulnerability that can be used to steal databases from ERP/CRM application Dolibarr.
Fortinet zero-day: Networking equipment vendor Fortinet says that a vulnerability it patched last week in one of its products was exploited by "an advanced actor" in "highly targeted" attacks at governmental or government-related organizations. The vulnerability—a zero-day at the time it was patched—is tracked as CVE-2022-41328 and described as a path traversal vulnerability that can lead to remote command execution on Fortinet devices that run versions 6.x and 7.x of the company's FortiOS operating system. Despite Fortinet disclosing the exploitation in a separate blog entry, the company's actual security advisory does not mention anything about this being exploited in the wild.
Firmware bugs dominate CISA KEV: An Eclypsium analysis of CISA's KEV catalog of actively-exploited bugs reveals that many of the security flaws exploited by threat actors in the wild are firmware and server software-related vulnerabilities.
Infosec industry
Blue Hat 2023 videos: Talks from the BlueHat 2023 security conference, which took place in early February, are now available on YouTube.
New tool—Zeus Cloud: A new security tool was released at the end of last year. The project is named Zeus Cloud and is described as a preventative cloud security platform that can help companies manage their cloud accounts and continuously monitor environments for misconfigurations and attack paths.